The Giza Pyramid Square History
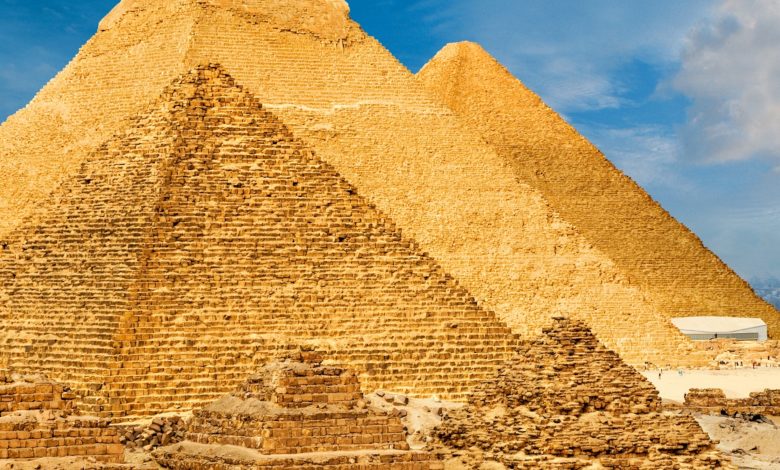

The Giza Pyramid Square, located in Egypt, dates back to the 26th century BCE. It features the Great Pyramid of Giza, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World.
The Giza Pyramid Square stands as an iconic symbol of ancient Egyptian civilization. Situated near Cairo, this archaeological marvel includes three main pyramids: the Great Pyramid of Khufu, the Pyramid of Khafre, and the Pyramid of Menkaure. Built during the Fourth Dynasty, these pyramids served as monumental tombs for Pharaohs.
The site also includes the enigmatic Sphinx, numerous smaller pyramids, and various tombs and temples. The precision in construction and alignment with celestial bodies continue to amaze researchers and visitors, showcasing the advanced engineering skills of ancient Egyptians.

Credit: www.archaeology.wiki
Origins Of Giza Pyramid Square
The Giza Pyramid Square is one of the world’s most fascinating sites. It stands as a testament to the brilliance of ancient Egyptian civilization. The pyramids, especially the Great Pyramid of Giza, have intrigued historians and tourists alike.
Ancient Egyptian Civilization
The ancient Egyptian civilization began over 5,000 years ago. It flourished along the Nile River. The Egyptians were skilled in many areas, including architecture, art, and engineering.
They built the Giza Pyramids as tombs for their pharaohs. The most famous is the Great Pyramid, built for Pharaoh Khufu. These structures are a testament to their advanced knowledge and skills.
Architectural Innovations
The Giza Pyramids are architectural marvels. They showcase the Egyptians’ innovative building techniques. The Great Pyramid consists of over 2 million stone blocks. Each block weighs several tons.
The precise alignment with the cardinal points is astonishing. The pyramids’ construction involved complex planning. Workers used simple tools yet achieved great precision.
They also developed unique methods to move and lift heavy stones. The ingenuity of their techniques remains a subject of study and admiration.
| Pyramid | Pharaoh | Height (meters) |
|---|---|---|
| Great Pyramid | Khufu | 146.6 |
| Pyramid of Khafre | Khafre | 136.4 |
| Pyramid of Menkaure | Menkaure | 65.5 |
- Great Pyramid: Oldest and largest
- Pyramid of Khafre: Second largest
- Pyramid of Menkaure: Smallest but still impressive
:focal(1280x975:1281x976)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/81/5a/815a3fdf-075c-468b-8acb-a84aec507502/jr.jpeg)
Credit: www.smithsonianmag.com
Construction Techniques
The construction of the Giza Pyramid Square remains a marvel. It showcases ancient engineering brilliance. This section explores the labor force, tools, and material sourcing.
Labor Force And Tools
Building the pyramids required many workers. Estimates suggest 20,000 to 30,000 laborers. They were skilled and unskilled workers. Some were artisans, masons, and laborers.
- Skilled Workers: They cut and shaped stones.
- Unskilled Laborers: They transported materials.
- Artisans: They decorated the interiors.
The tools used were simple yet effective. Workers used copper chisels, wooden mallets, and stone hammers.
| Tool | Usage |
|---|---|
| Copper Chisels | Cutting and shaping stones |
| Wooden Mallets | Hitting chisels |
| Stone Hammers | Breaking larger stones |
Material Sourcing
The materials were sourced locally and from afar. The primary material was limestone. It came from nearby quarries. The harder granite came from Aswan, 500 miles away.
- Limestone: Used for the bulk of the pyramid.
- Granite: Used for the inner chambers and passages.
- Mortar: Made from gypsum or lime.
The transportation of these materials was a major task. Workers used sledges and rolling logs. They also used the Nile River for transportation.
The construction techniques of the Giza Pyramid Square show human ingenuity. They reflect the dedication and skill of the ancient Egyptians.
Cultural Significance
The Giza Pyramid Square is one of the most iconic sites in the world. Its cultural significance spans ancient civilizations and modern times. Let’s explore the profound impact it has had on religious beliefs and societal structures.
Religious Beliefs
The Giza Pyramids were built as tombs for the pharaohs. Ancient Egyptians believed in an afterlife. The pyramids were meant to help pharaohs in their journey to the afterlife. They thought the pyramids were a stairway to the heavens.
The Sphinx, also located at Giza, has religious significance. It’s believed to be a guardian of the pyramids. The Sphinx combines the body of a lion and the head of a human. This symbolizes strength and wisdom.
Societal Impact
The construction of the pyramids showed the power of the pharaohs. Building them required a large workforce. This workforce included skilled laborers, artisans, and farmers. The project united many people for a common goal.
The Giza Pyramids influenced architecture around the world. Modern buildings often draw inspiration from pyramid shapes. The structure of the pyramids showcased advanced engineering skills. These skills were passed down through generations.
The pyramids also became a symbol of Egypt itself. They attract millions of tourists each year. This boosts Egypt’s economy and cultural pride.
Modern Discoveries
The Giza Pyramid Square has always fascinated historians and archaeologists. In recent years, modern discoveries have shed new light on this ancient marvel. These findings help us understand how the pyramids were built and their purpose.
Archaeological Finds
Recent archaeological finds have unveiled hidden chambers and artifacts. Scientists discovered secret rooms using advanced scanning technology. These rooms are believed to hold treasures and ancient texts. Excavations have revealed new tools used by the builders. This helps us understand the construction techniques better.
Pottery shards and ancient tools were also found near the pyramids. These items tell us about the daily lives of the workers. Some of the tools were made from copper and stone. These discoveries give us a clearer picture of ancient Egyptian life.
Technological Advances
Technological advances have revolutionized the study of the pyramids. Scientists now use drones to map the area. These drones provide high-resolution images of the pyramid’s structure. Laser scanning technology helps in creating detailed 3D models. These models are crucial for understanding the pyramid’s complex design.
Ground-penetrating radar is another tool used by researchers. This technology helps in detecting hidden chambers and tunnels. It provides a non-invasive way to explore the pyramids. The use of these advanced tools has led to many groundbreaking discoveries.
| Discovery | Significance |
|---|---|
| Hidden Chambers | Potentially holds treasures and ancient texts |
| Pottery Shards | Insights into daily lives of workers |
| 3D Models | Understanding pyramid’s complex design |
These modern discoveries continue to enrich our knowledge. They help us appreciate the genius of ancient Egyptian builders. Stay tuned for more updates as technology unveils new secrets.

Credit: www.nationalgeographic.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The History Of Giza Pyramid?
The Giza Pyramid, built around 2580–2560 BC, served as Pharaoh Khufu’s tomb and showcases ancient Egyptian engineering.
Who Built The Giza Pyramids?
The Giza Pyramids were constructed by ancient Egyptians, specifically during the reign of Pharaoh Khufu.
Why Was The Giza Pyramid Built?
The Giza Pyramid was built as a monumental tomb for Pharaoh Khufu, to honor and preserve his legacy.
How Long Did It Take To Build Giza Pyramid?
It took approximately 20 years to build the Giza Pyramid, using a large workforce of skilled laborers and slaves.
Conclusion
The Giza Pyramid Square holds a captivating history that continues to inspire awe. Its architectural marvels and ancient significance attract scholars and tourists alike. Discovering its mysteries deepens our appreciation for human ingenuity. Visiting this iconic site offers a glimpse into a rich cultural heritage.
Explore Giza and experience history come alive.