Machu Picchu History.

Machu Picchu, built in the 15th century by the Inca emperor Pachacuti, is a UNESCO World Heritage site in Peru. It is renowned for its archaeological significance and stunning natural scenery.
Machu Picchu, nestled in the Andes Mountains, is one of the most iconic archaeological sites in the world. The Inca emperor Pachacuti built this ancient city in the 15th century. Hidden from the outside world for centuries, it was rediscovered in 1911 by American historian Hiram Bingham.
The site offers a glimpse into the sophisticated engineering and architectural prowess of the Inca civilization. Visitors marvel at its well-preserved terraces, temples, and intricate stonework. Machu Picchu remains a testament to the ingenuity and cultural heritage of the Incas, attracting millions of tourists annually.
Ancient Origins
Machu Picchu is a famous ancient city. Its origins date back to the 15th century. The Inca Empire built it high in the Andes Mountains. This city is a symbol of the Inca’s advanced knowledge.
Inca Empire
The Inca Empire was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. It extended from present-day Ecuador to Chile. The Incas were skilled farmers, builders, and engineers.
The Incas built Machu Picchu during the reign of Emperor Pachacuti. The city served as a royal estate and religious site. Only a select few lived in this sacred place.
Construction Techniques
The construction of Machu Picchu showcases incredible engineering skills. The Incas used a technique called ashlar masonry. They cut stones to fit perfectly without mortar.
This method made the structures strong and earthquake-resistant. The Incas also created advanced irrigation systems. These systems provided water to the terraces and crops.
The terraces at Machu Picchu helped prevent erosion. They also provided space for farming. The Incas used simple tools made of stone, wood, and bronze.
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Ashlar Masonry | Stones cut to fit perfectly without mortar. |
| Irrigation Systems | Advanced systems to provide water to crops. |
| Terraces | Prevent erosion and provide farming space. |
Machu Picchu remains a testament to Inca ingenuity. The city’s design and construction continue to amaze people today.

Credit: www.nationalgeographic.com
Discovery And Excavation
The mysterious ruins of Machu Picchu lay hidden for centuries. It was not until the early 20th century that the world took notice of this ancient site. The discovery and excavation of Machu Picchu uncovered many secrets of the Inca civilization.
Hiram Bingham
In 1911, Hiram Bingham, an American historian, stumbled upon Machu Picchu. He was led to the site by a local farmer. Bingham was amazed by what he found. The ruins were covered in dense vegetation.
Bingham’s discovery brought Machu Picchu to international attention. He soon organized an expedition to excavate the site. His team worked tirelessly to uncover the hidden structures.
Archaeological Findings
During the excavation, many archaeological findings were made. The team uncovered houses, temples, and terraces. They found pottery, tools, and other artifacts.
The most important discovery was the Intihuatana stone. This stone was likely used as an astronomical clock. Other notable finds included the Temple of the Sun and the Room of the Three Windows.
These findings provided valuable insight into Inca culture. The artifacts helped scholars understand the daily lives of the Inca people.
| Key Discoveries | Description |
|---|---|
| Intihuatana Stone | Likely used as an astronomical clock. |
| Temple of the Sun | Religious site for the Incas. |
| Room of the Three Windows | Important ceremonial room. |
- Hiram Bingham discovered Machu Picchu in 1911.
- The site was covered in dense vegetation.
- Excavations revealed houses, temples, and terraces.
- Key finds include the Intihuatana stone and the Temple of the Sun.
Cultural Significance
The cultural significance of Machu Picchu is profound. This ancient city holds deep meaning for the Incan civilization. It symbolizes their technological prowess and spiritual beliefs. Let’s explore its religious importance and agricultural practices.
Religious Importance
Machu Picchu was a sacred place. The Incas worshipped the sun god, Inti. They built many temples here. The most famous is the Temple of the Sun. Priests performed rituals here to honor their gods.
Another important site is the Intihuatana Stone. This stone was used as an astronomical clock. It helped the Incas predict solstices. They believed it had magical powers.
Agricultural Practices
The Incas were skilled farmers. They used terrace farming to grow crops. These terraces prevented soil erosion. They also created a unique irrigation system.
The main crops were potatoes and maize. They also grew quinoa and coca leaves. The Incas stored food in special buildings called qollqas.
| Crop | Usage |
|---|---|
| Potatoes | Staple food |
| Maize | Food and rituals |
| Quinoa | Nutritious grain |
| Coca leaves | Medicinal and ritualistic |
These practices showed their advanced agricultural knowledge. They knew how to adapt to their environment.

Credit: www.britannica.com
Modern-day Machu Picchu
Machu Picchu, a marvel of Incan civilization, continues to fascinate in modern times. This ancient site is a blend of history, culture, and breathtaking scenery. Its allure draws visitors from around the globe. Yet, with this influx, the site faces both opportunities and challenges.
Tourism Impact
The rise in tourism has reshaped Machu Picchu. Every year, nearly 1.5 million people visit. This surge benefits the local economy through job creation and business growth. Tour guides, hotels, and restaurants thrive due to the influx.
However, heavy foot traffic puts strain on the site. Ancient pathways wear down and structures face damage. The environmental footprint increases with more visitors. Balancing tourism and preservation becomes essential.
Conservation Efforts
Preservation is crucial for Machu Picchu’s future. Various measures have been implemented. Visitor limits are now enforced to reduce wear and tear. These limits help maintain the site’s integrity.
Local authorities and international organizations collaborate on conservation. Advanced technology monitors the site’s condition. Restoration projects repair damaged areas. Education programs raise awareness about the site’s significance. These efforts ensure Machu Picchu endures for future generations.
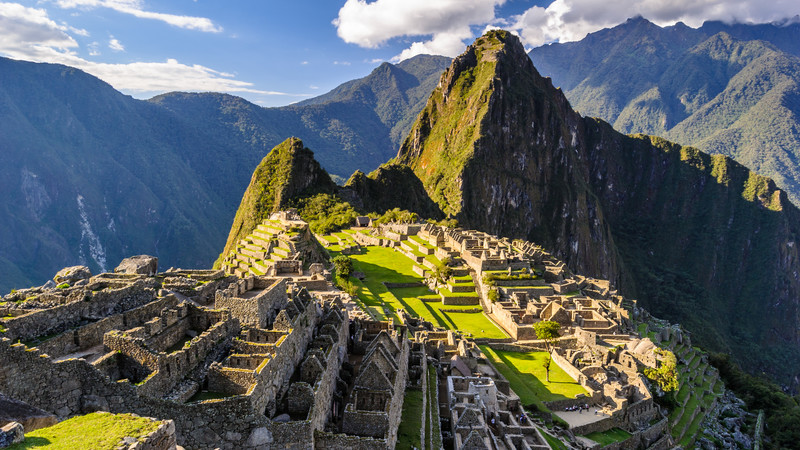

Credit: www.intrepidtravel.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The History Of Machu Picchu?
Machu Picchu was built in the 15th century by the Inca emperor Pachacuti.
Who Discovered Machu Picchu?
Hiram Bingham, an American historian, rediscovered Machu Picchu in 1911.
Why Is Machu Picchu Significant?
Machu Picchu is a UNESCO World Heritage site, showcasing incredible Inca architecture and engineering.
How Was Machu Picchu Constructed?
Machu Picchu was constructed using dry-stone masonry techniques, fitting stones together without mortar.
Conclusion
Machu Picchu’s history captivates and inspires with its ancient mysteries. This iconic site symbolizes the Inca Empire’s grandeur. Understanding its past enriches our appreciation for this UNESCO World Heritage site. Visit Machu Picchu to experience its breathtaking beauty and historical significance firsthand.
Dive into its rich legacy and uncover the secrets of this majestic wonder.