Introduction And History of the Republic of Genoa: A Fascinating Journey
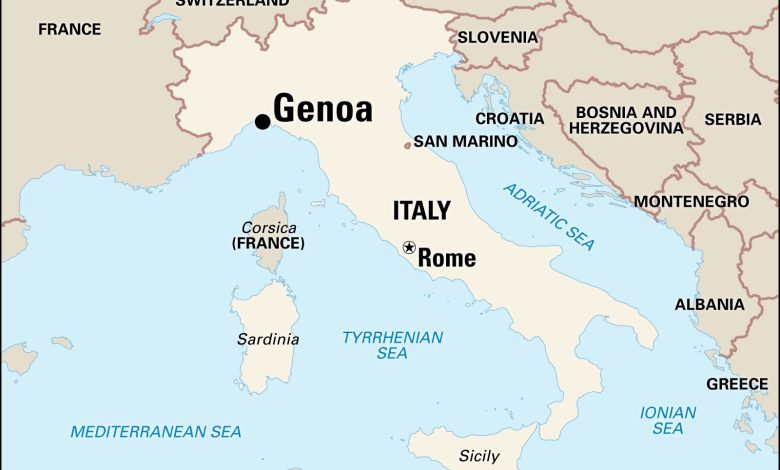
The Republic of Genoa was a powerful maritime state. It existed from the 11th century to the 18th century. Genoa was located in what is now Italy.
Early Beginnings
Genoa started as a small fishing village. Its location on the Ligurian Sea helped it grow. The people of Genoa were excellent sailors and traders.

Credit: www.berghahnbooks.com
The Rise of Genoa
By the 11th century, Genoa had become a powerful city-state. It had a strong navy and many trading ships. The people traded goods with other countries. They became wealthy and influential.
Trade And Commerce
Genoa traded with many countries around the Mediterranean Sea. They traded goods like silk, spices, and gold. This made the city very rich.
- Silk from Asia
- Spices from the Middle East
- Gold from Africa
Exploration And Expansion
Genoa was also known for its explorers. They discovered new lands and new trade routes. One famous explorer from Genoa was Christopher Columbus. He discovered America in 1492.
The Government of Genoa
Genoa had a unique government. It was a republic, which means it was ruled by elected officials. The leaders were called Doges. They were chosen by the people of Genoa.
The Council
The government also had a council. The council helped make decisions for the city. They worked together to keep Genoa strong and safe.
| Position | Role |
|---|---|
| Doge | Leader of the Republic |
| Council Member | Advisor and Decision Maker |

Credit: link.springer.com
The Golden Age
Genoa’s golden age was during the 12th to 14th centuries. During this time, Genoa was very powerful. It had many colonies and trading posts around the world.
Colonies And Trading Posts
Genoa had colonies in places like Crimea, Corsica, and Sardinia. These colonies helped Genoa control trade routes and gain more wealth.
- Crimea
- Corsica
- Sardinia
Rivalry With Venice
Genoa had a rivalry with another powerful city-state, Venice. Both cities wanted to control the trade routes. This led to many wars between them.
The Decline of Genoa
Genoa’s power began to decline in the 15th century. Many factors contributed to this decline.
Wars And Conflicts
Genoa was involved in many wars. These wars weakened the city and its economy. The rivalry with Venice was especially damaging.
Economic Problems
Genoa also faced economic problems. New trade routes were discovered, and Genoa lost control of some of its colonies. This led to a decline in wealth.
The End of the Republic
The Republic of Genoa came to an end in 1797. Napoleon Bonaparte, a French military leader, conquered the city. Genoa became part of the French Empire.
Legacy of the Republic of Genoa
The Republic of Genoa left a lasting legacy. It was known for its maritime power and trade. The city of Genoa is still a major port in Italy today.
Architecture And Culture
Genoa is known for its beautiful architecture. Many buildings from the Republic’s time still stand today. The culture of Genoa also influenced many parts of Europe.
Famous People
Many famous people came from Genoa. This includes explorers like Christopher Columbus and artists like Andrea Doria.
- Christopher Columbus
- Andrea Doria
Modern Genoa
Today, Genoa is a vibrant city in Italy. It is known for its history, culture, and beautiful port. The legacy of the Republic of Genoa lives on.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Republic Of Genoa?
The Republic of Genoa was a powerful maritime republic in Italy.
When Was The Republic Of Genoa Founded?
The Republic of Genoa was founded in 1005 AD.
What Made Genoa Wealthy?
Genoa became wealthy through trade and banking.
Who Were The Genoese?
The Genoese were the people of the Republic of Genoa.
Conclusion
The Republic of Genoa was a powerful and influential state. Its history is filled with exploration, trade, and culture. Though it no longer exists, its legacy continues to shape the world.