Introduction And History of Papal States: A Fascinating Journey
The Papal States hold a special place in history. They were lands ruled by the Pope. Let’s dive into their fascinating story.
What Were the Papal States?
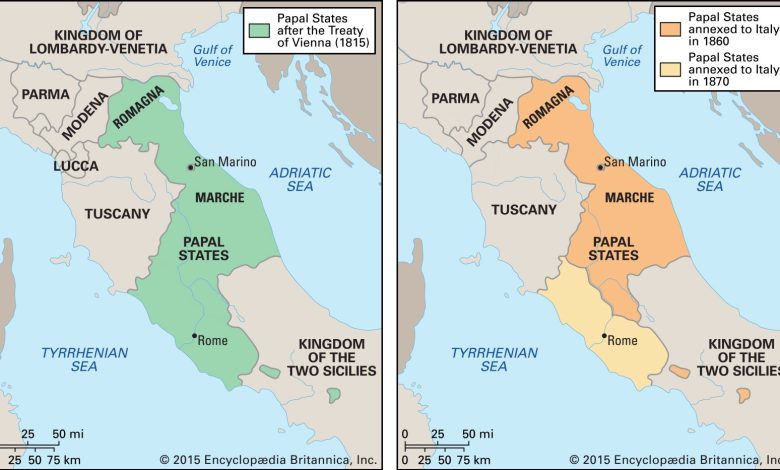
The Papal States were territories in central Italy. The Pope governed these lands from 754 AD to 1870 AD. The Pope is the leader of the Catholic Church.
Why Were They Important?
The Papal States were very important. They were a center of religion and power. The Pope had both spiritual and political influence.
Early Beginnings
In the 4th century, Christianity grew in Rome. Constantine, a Roman Emperor, made Christianity legal. This set the stage for the Church’s rise.
Donation Of Pepin
The real start of the Papal States was in 754 AD. Pepin the Short, a Frankish king, gave land to the Pope. This gift was called the Donation of Pepin.

Credit: www.medievalists.net
Growth and Expansion
Over time, the Papal States grew. More land was added. The Pope became a powerful ruler.
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 754 AD | Donation of Pepin |
| 800 AD | Charlemagne crowned as Emperor |
| 1054 AD | Great Schism |
| 1309-1377 AD | Avignon Papacy |
| 1870 AD | End of Papal States |
Challenges and Conflicts
The Papal States faced many challenges. There were wars and conflicts. Other rulers wanted the land. The Pope had to defend it.
Great Schism
In 1054, the Christian Church split. It became the Roman Catholic Church and the Eastern Orthodox Church. This was called the Great Schism.
Avignon Papacy
From 1309 to 1377, the Pope lived in Avignon, France. This period was known as the Avignon Papacy. It weakened the Papal States.

Credit: www.britannica.com
Renaissance and Reformation
The Renaissance was a time of great change. It began in the 14th century. Art, science, and culture flourished. The Papal States played a key role.
Patrons Of Art
The Popes were patrons of the arts. They supported artists like Michelangelo and Raphael. This made Rome a center of culture.
Reformation
In the 16th century, the Reformation began. It was a movement against the Catholic Church. Martin Luther was a key figure. This led to the rise of Protestantism.
Modern Era
The 19th century brought more challenges. Italy was unifying as a nation. The Papal States were in the way.
End Of Papal States
In 1870, the Papal States ended. Italian forces took over Rome. The Pope lost his temporal power.
Vatican City
In 1929, the Lateran Treaty was signed. It created Vatican City. The Pope now rules this small city-state.
Legacy
The Papal States had a lasting impact. They shaped the history of Italy and the Catholic Church. Today, Vatican City continues this legacy.
Influence On Culture
The Papal States influenced art, culture, and religion. They were a beacon of learning and creativity. Their impact is still felt today.
Political Significance
The Papal States were a political power. They played a key role in European politics. The Pope was a significant figure in global affairs.
Religious Importance
The Papal States were the heart of the Catholic Church. They were a spiritual center for millions of believers. The Pope’s influence reached far and wide.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Were The Papal States?
The Papal States were territories in central Italy under the Pope’s rule.
When Did The Papal States Exist?
The Papal States existed from 754 AD to 1870 AD.
How Did The Papal States Form?
The Papal States formed through donations and conquests by the Church.
Why Did The Papal States End?
The Papal States ended due to Italian unification in 1870.
Conclusion
The history of the Papal States is rich and complex. From their early beginnings to their end, they left a mark on the world. Understanding their history helps us appreciate their legacy.
Thank you for reading about the Papal States. We hope you found this journey through history enlightening. Keep exploring and learning!