United Nations Member States of Awe-Inspiring Description.
The United Nations (UN) consists of 193 member states.

United Nations Member States – the joined together countries’ part states contain 193 United Nations Member States. The international community officially recognizes the sovereignty of every single part state nation within the United Nations Member States.
United Nations Member States at its establishment in 1945:
The United Nations Member States collectively work towards global peace and security.
Each United Nations Member State contributes to the goals of the organization.
Since 1945, the United Nations Member States have played a pivotal role in global governance.
the Signed Up Countries built a system to advance peace and security alongside international social participation. United Matter harvesting 193 using which provides representation to every country in the world. Members unite their efforts to resolve international problems, especially poverty, environmental changes, and human rights violations.
The Common Gathering together with Security Chamber and other entities facilitate exchange and decision-making processes. The United Nations takes part in security maintenance operations along with humanitarian support activities.
The multicultural structure of this organization drives international teamwork to create a better and fairer international environment. A state that engages with the UN demonstrates its dedication to embrace the recognized principles and targets of the organization.

Credit: www.un.org
With 193 United Nations Member States, the organization represents a vast array of cultures and perspectives.
Each of brings its unique challenges and opportunities to the table.
The establishment of the United Nations Member States marked a significant turning point in international relations.
The United Nations Member States strive to uphold the principles of peace and security.
As members of the United Nations Member States, countries work together to enhance global cooperation.
The collaborate extensively to tackle global challenges.
The United Nations Member State adhere to a set of core values that guide their missions.
United Nations Member State Each has a role in shaping international norms and policies.
The United Nations Member State cooperation among is essential for addressing global crises.
The United Nations Member State champion human rights and social justice.
Each of contributes to a collective response to humanitarian needs.
Focus on the well-being and rights of people globally.
Through their efforts, United Nations Member State aim to foster sustainable development worldwide.
United Nations Member States Presentation To The Joined together Nations:
As a world substance, the countries that joined together have capacities as a worldwide organization—the organization’s capacity to join together states for peace upkeep and security conservation.
The geographical representation of United Nations Member States is critical for fair global dialogue.
The Joined Together Countries exist to promote human rights and social progress. The organization came into existence promptly after World War II. Nowadays, it incorporates 193 part states. States inside the organization collaborate to make changes worldwide.
Formation And Purpose United Nations Member States:
The Joined together Countries formally set up themselves on October 24 1945. The essential mission of this organization served to halt assist fighting. The victory of the Joined Together Countries activity has since the Alliance of Countries demonstrated its inability to succeed.
Economic profiles among United Nations Member States illustrate diverse development paths.
Fifty world countries assembled in San Francisco to start the preparation. They marked the UN Constitution. The record gives both destinations and authoritative strategies of the Joined together Nations.
Every part gets the principal objective behind the countries that joined together. The organization exists to protect peace between countries around the world. The organization makes positive connections between distinctive nations.
The organization empowers social change and provides an economical standard of living for everyone. The Joined Together Countries spend their endeavors tending to issues related to climate change, well-being, and instruction challenges.
United Nations Member States Core Principles:
The UN depends on a characterized set of center values to conduct its operations. The organization employs these measures to coordinate its operational choices and key choices.
The joined together countries apply an added balance to their part countries. All issues require one to discover one’s determination through serene means.
When taking after non-intervention conventions, the joined countries will not enter household realms. The organization advances group exertion between countries to address world challenges.
Read more – World Community
The countries that joined together effectively employ human rights as their central centre. As a centre conviction, the organization ensures everybody’s human rights by providing opportunities and correspondence.
The Inclusive Statement of Human Rights authoritatively came into presence in 1948. Each individual has these essential flexibility and rights agreeing to this document.
The standards empower the Joined-together Countries to fulfill their organizational purposes. The organization maintains a framework that conveys blessedness and empowers collaborative hones between distinctive states.
Credit: en.wikipedia.org
United Nations Member State Geological Distribution:
The UN is a worldwide organization comprised of part states speaking to each landmass. It exists beneath the title of the joined-together Countries.
Understanding the UN’s assorted representation requires a point-by-point examination of how its part states are dispersed worldwide. This section assesses the territorial groupings and mainland representation of all joined-together Country part states.
All part states of the Joined together Countries have a place in five formally recognized territorial bunches. The bunches back both talk and choice forms. The bunches are:
- African Group
- Asia-Pacific Group
- Eastern European Group
- Latin American and Caribbean Group
- Western European and Others Group
One cluster of countries inside each gathers keeps up standard geographic foundations. Through these bunches, the UN maintains adjusted cooperation over its distinctive organizations.
Continental Representation:
Membership in the Group of Countries includes different countries speaking to distinctive landmasses. The table below uncovers how numerous part states have a place in each landmass.
| Continent | Number of Member States |
|---|---|
| Africa | 54 |
| Asia | 48 |
| Europe | 44 |
| Latin America and Caribbean | 33 |
| North America | 2 |
| Oceania | 14 |
Africa has the highest number of member states. North America has the least. This distribution highlights the global reach of the UN.
The representation ensures that all continents have a voice in global matters.
United Nations Member States Economic Profiles:
A broad spectrum of economic conditions exists between member states affiliated with the United Nations. All nations exhibit distinct economic systems between themselves. The globally varying economic conditions create steps toward a better understanding of the worldwide economy.
Developed Nations:
Nations that have attained developed status maintain economically solid systems with diversified sectors. The economies in these regions have achieved significant financial revenue and elaborate infrastructure systems. Well-established industries and service-based sectors function throughout these countries.
Because of its multiple economic sectors, the United States ranks as an economy with diverse industries. This country’s primary economic sectors consist of technology, finance, and healthcare services.
The world recognizes Germany through its remarkable capability in design and production engineering. Its automotive industry is world-renowned.
Japan stands out because of its world-class technology production and renowned automobile industry. In addition to its existing infrastructure, the country operates a strong service sector.
United Nations Member States Developing Countries:
These countries work toward developing their economic frameworks. These countries possess expanding business sectors while their markets are active. Each of these countries deals with distinctive opportunities together with unique difficulties.
India’s economy expands rapidly each year. Information technology and the agricultural sectors are the core industries in this nation.
Nigeria’s resources extend across its territory, forming natural wealth. The nation’s survival heavily relies on its oil industry.
Brazil has an economy that covers various industries. Agriculture, mining, and services form the major economic sectors in the country.
An easy reference comparison of economic indicators exists in this table:
| Country | GDP (in billion USD) | Major Industries |
|---|---|---|
| United States | 21,430 | Technology, Finance, Healthcare |
| Germany | 4,200 | Automotive, Engineering, Manufacturing |
| Japan | 5,080 | Technology, Automobile, Services |
| India | 2,870 | Information Technology, Agriculture |
| Nigeria | 448 | Oil, Agriculture, Mining |
| Brazil | 2,055 | Agriculture, Mining, Services |
The social diversity of United Nations Member States enriches global culture and understanding.
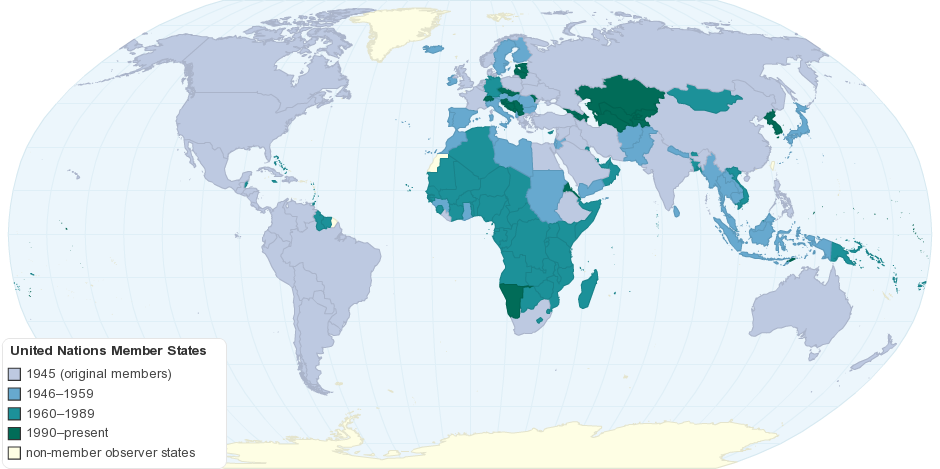
Credit: chartsbin.com
United Nations Member States Social Diversity:
Among its numerous characteristics, the Joined Countries stand out because they contain a wide range of social histories. Each Joined Country part of the state contributes its unmistakable social legacy, conventional ways of thinking, and devout convictions. The UN benefits from this auxiliary abundance, which makes it a dynamic, flourishing organization.
Languages And Traditions:
All Joined together. Countries and nations utilize assorted phonetic frameworks. Numerous dialects inside the countries that joined together speak to unmistakable social hones from over each country state. Each country has a single official language and different official dialects.
- China: Mandarin
- India: Hindi, English, and 21 other languages
- Spain: Spanish, Catalan, Galician, Basque
A dialect comes with its particular conventional legacy. Spanish inhabitants watch La Tomatina as part of their social conventions. Diwali is one of the most significant celebrations in India. The conventions over distinctive communities contribute differing colors to our worldwide society.
Languages and traditions among United Nations Member States showcase rich heritages.
Religious practices within United Nations Member States underline the importance of respect and tolerance.
Political systems among United Nations Member States vary widely, influencing governance and stability.
United Nations Member States Religious Practices:
Different categories of religion exist throughout the member states of the Joined Countries. Individuals’ daily schedules infer their shape from these recognized traditions. Worldwide dialects impact the foundation of open celebrations, which characterize conventional traditions for each country.
Political Systems:
Participating states in the United Nations display different political systems from each other. National institutions across countries establish their forms of governing systems. Different governance systems develop the degree of stability found within these countries. Understanding different political formations provides the necessary knowledge for understanding worldwide political operations.
Types Of Governance:
Each member nation of the United Countries runs under its specific political system. The most common sorts include:
Democracies: Individuals choose their leaders.
Monarchies: A ruler or ruler rules.
The decision-making processes of United Nations Member States reflect their diverse political contexts.
A single person and a small group of power members form an authoritarian administration.
These political systems unite major features between democratic systems and authoritarian leadership.
Several states belong to specific governmental classifications. Particular political characteristics in these systems form how nations execute their politics.
Political stability among United Nations Member States is vital for effective governance.
Political Stability:
A nation needs political stability to achieve proper growth and development. States with stable rules usually establish strong governmental systems. Stable countries ensure the establishment of law, organize societal development and foster financial growth.
The table below shows illustrations of countries implementing various levels of political stability
| Country | Major Religion | Key Festival |
|---|---|---|
| Saudi Arabia | Islam | Ramadan |
| Brazil | Christianity | Carnival |
| Thailand | Buddhism | Songkran |
These religious practices promote peace and understanding. They also highlight the importance of respecting different beliefs. The UN encourages this respect through various initiatives.
Political stability
| Country | Type of Governance | Political Stability |
|---|---|---|
| Canada | Democracy | High |
| Saudi Arabia | Monarchy | Moderate |
| North Korea | Authoritarian | Low |
Political stability impacts various aspects of life. It influences economic policies, social harmony, and international relations.
Human Development Indicators:
The Human Development Indicators monitor different national progress sectors. The three leading indicators that measure national development are education systems, healthcare delivery, and quality of living standards. The Human Development Indicators provide information about the living standards in countries that belong to the United Nations.
The academic level of education differs substantially across nations that belong to the United Nations. Advanced education systems and high literacy rates exist in certain countries. Several nations encounter obstacles when it comes to obtaining minimum educational services.
High Literacy Rates: Countries like Norway and Japan boast near-universal literacy.
Basic Education Access: Nations such as Chad and Niger struggle with primary education access.
Investments in education lead to better job opportunities and economic growth. Governments with excellent education institutions tend to generate higher national GDP’s.
| Country | Literacy Rate |
|---|---|
| Norway | 99% |
| Japan | 99% |
| Chad | 22% |
| Niger | 19% |
Healthcare Systems:
Healthcare systems exhibit substantial differences between those found within United Nations member countries. Select countries provide nationwide healthcare services, but many states restrict access to medical care.
Under Universal Healthcare systems, Sweden and Canada deliver medical assistance to their entire citizen population.
Limited Services: Countries such as Afghanistan and Somalia lack basic healthcare facilities.
Healthcare systems that strongly support patients enable longer life expectancies and decrease the number of diseases. Dangerous health conditions tend to decrease in nations that offer complete healthcare services, and these countries also show increased happiness levels.
| Country | Life Expectancy |
|---|---|
| Sweden | 82 years |
| Canada | 82 years |
| Afghanistan | 60 years |
| Somalia | 58 years |
Understanding the role of United Nations Member States is crucial for international relations.
Environmental Challenges:
All United Nations member countries encounter substantial environmental problems. The problems affect both the population and economic structures of these territories. The discussion focuses on two principal factors: Climate Change Impact definable Development.
Climate Change Impact:
Climate change impacts all countries. Multiple countries now face elevated weather intensity in their territories. The region experiences three major environmental events: hurricanes, floods, and droughts. Such events wipe out houses together with agricultural production. The crises force many individuals to lose their residence and professional income.
Read more – What is the Difference between United Nations And NATO: Key Distinctions.
Rising temperatures also harm wildlife. Natural species face great difficulties in their efforts to survive. Both glaciers and ocean water are melting simultaneously. The oceanfront zones stand vulnerable to flooding dangers. The situation forces residents to relocate from their initial residences.
A table displays climate change difficulties faced by various nations worldwide.
| Country | Climate Challenge |
|---|---|
| Bangladesh | Frequent floods |
| Australia | Severe droughts |
| Maldives | Rising sea levels |
| Canada | Melting glaciers |
Sustainable Development:
Sustainable development is essential for resolving these problems. It means using resources wisely. The approach protects the ability of upcoming generations to succeed. Several nations now focus on building sustainable energy alternatives. The common choices among energy production sectors exist between wind and solar power.
Numerous nations support sustainable agriculture practices during their national initiatives. Such measures decrease the need for dangerous chemicals. Such practices conserve both water resources and land-soil components. The protection of forests in certain countries exists to prevent and fight climate change.
These supportive measures receive backing from the United Nations. These institutions have established specific targets to support sustainable development. New goals enable countries to choose eco-friendly options in their decision-making process.
These represent the sustainable development goals:
- End poverty
Ensure healthy lives
Promote sustainable agriculture
Provide clean water and sanitation
Use affordable and clean energy
Worldwide Cooperation:
Global participation is the spine of the joined-together Countries. Part states work together to guarantee peace, security, and advancement worldwide. They share assets, information, and mastery to handle worldwide challenges. Underneath are a few of the essential perspectives of this cooperation.
Peacekeeping Missions:
Peacekeeping missions are a noteworthy perspective of worldwide participation. The countries that joined together send peacekeepers to strife zones. Their objective is to anticipate viciousness and secure civilians. Peacekeepers come from different parts of the state. They work beneath a bound-together command. These missions advance soundness and revamp beliefs among communities.
Peacekeeping missions have a few components:
Military Operations: Keep up security and hinder violence.
Civilian Police: Prepare nearby police forces.
Humanitarian Help: Give essential needs and therapeutic care.
International Aid:
International help is another pivotal component of worldwide participation. Part states pool assets to back nations in require. Help can be budgetary, specialized, or compassionate. This back makes a difference when countries recoup from fiasco and clashes. It, too, advances feasible development.
Here is a table summarizing sorts of universal help:
| Type of Aid | Description |
|---|---|
| Financial Aid | Funds for economic development and recovery. |
| Technical Aid | Expertise and technology transfer. |
| Humanitarian Aid | Emergency relief and basic necessities. |
International aid efforts ensure no nation is left behind. They foster global stability and prosperity.
F A Q
What Is Implied By Part States Of United Nations Member States?
Member states of the Joined Together Countries are nations that have joined the UN and agree to maintain its standards and goals.
What Are The Depictions Of The Joined together Nations?
The Joined together Countries is a universal organization established in 1945. It advances peace, security, and participation among part nations. The UN addresses worldwide issues such as human rights, climate change, and maintainable advancement. Its fundamental bodies incorporate the Common Gathering, Security Chamber, and Universal Court of Justice.
Who Are The Part States Of The Un And How Numerous Are There?
The UN has 193 part states. These incorporate nearly all globally recognized nations. The most current part is South Sudan.
Which Un Body Incorporates All 193 Part States?
The UN Common Gathering incorporates all 193 part states. It serves as a gathering for multilateral discourse on worldwide issues.
Understanding the fascinating perspectives of each joined-together country part of the state cultivates worldwide solidarity. These nations bring differing societies and points of view—their collaboration upgrades worldwide peace and advancement. Locking in with their stories improves our worldwide mindfulness. Remain educated and celebrate the world’s differing qualities through the countries joined together as part states.




