The Great Wall of China History
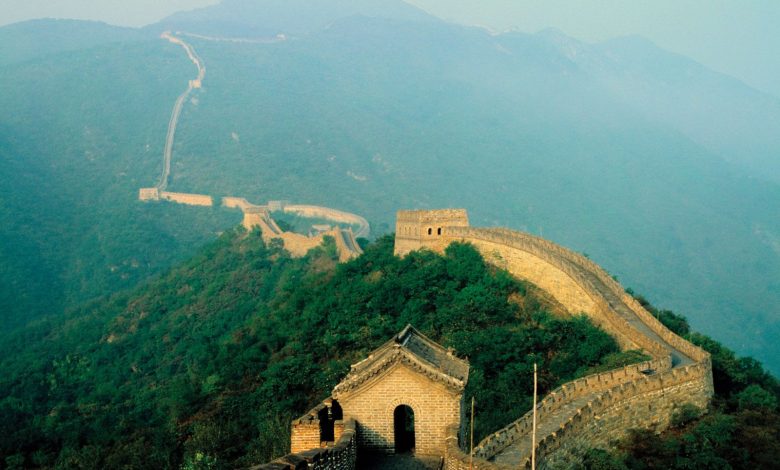

The Great Wall of China dates back to the 7th century BC. It was built to protect against invasions and raids.
The Great Wall of China is an iconic symbol of ancient engineering and fortification. Stretching over 13,000 miles, it traverses rugged mountains, vast deserts, and lush plains. Construction began during the Qin Dynasty and continued through the Ming Dynasty. The wall was primarily built to guard against Mongol invasions.
Made from various materials like earth, wood, bricks, and stone, it showcases diverse construction techniques. Today, it stands as a testament to China’s historical resilience and architectural prowess. Visitors from around the world marvel at this monumental structure, making it a significant cultural and historical landmark.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Origins And Construction
The Great Wall of China is a marvel of ancient engineering. Its origins and construction showcase the ingenuity and determination of early Chinese civilizations. This section delves into the early walls and unified efforts that brought this colossal structure to life.
Early Walls
Before the Great Wall as we know it, there were smaller walls. These early walls were built by various states during the Warring States Period (475-221 BC). The purpose was to defend against invasions and raids by nomadic tribes.
These walls were mainly made of earth and wood. They were effective in their time but lacked the durability of later constructions. Each state built its own walls, so there was no unified structure.
| State | Materials Used | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Qi | Earth and Wood | Defense against Yan |
| Yan | Earth and Wood | Defense against Zhao |
| Zhao | Earth and Wood | Defense against Xiongnu |
Unified Efforts
The first unified efforts to build the Great Wall began under Emperor Qin Shi Huang (221-210 BC). He unified China and sought to protect it from northern invaders.
Qin Shi Huang ordered the connection of existing walls and the construction of new sections. This effort required hundreds of thousands of laborers, including soldiers, prisoners, and commoners. The construction materials evolved to include stone and bricks, which provided greater strength and durability.
Under subsequent dynasties, the wall was extended and fortified. The Ming Dynasty (1368-1644) made significant enhancements, using bricks and stone extensively and adding watchtowers and fortresses.
- Qin Dynasty: Connected existing walls
- Han Dynasty: Extended westward
- Ming Dynasty: Enhanced with bricks and stone
These unified efforts transformed the Great Wall into the iconic structure we recognize today. It stands as a testament to the determination and engineering prowess of ancient China.

Credit: education.nationalgeographic.org
Dynasties And Development
The Great Wall of China has a long history. It was built over many centuries by different dynasties. Each dynasty added its own touch. This made the wall unique. Let’s explore two key periods: the Qin Dynasty and the Ming Dynasty Enhancements.
Qin Dynasty
The Qin Dynasty began the construction of the Great Wall. The first emperor, Qin Shi Huang, started building in 221 BC. He wanted to protect his empire from invaders. The wall during this time was made of earth and wood.
The Qin Wall was not as strong as later versions. It covered a distance of about 5,000 kilometers. Soldiers were stationed along the wall. They kept watch for enemies. The wall also had signal fires to send messages.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Material | Earth and Wood |
| Length | 5,000 kilometers |
| Purpose | Defense |
Ming Dynasty Enhancements
The Ming Dynasty made the wall stronger. This period lasted from 1368 to 1644. They used bricks and stones. The wall became more durable and impressive.
The Ming Wall had many watchtowers. These towers were used for surveillance and storage. Ming rulers expanded the wall to 8,850 kilometers. They also built fortresses along the wall.
- Bricks and stones used for construction
- Length extended to 8,850 kilometers
- Numerous watchtowers added
- Fortresses built for extra defense
These enhancements made the wall a strong barrier. It protected China from invasions for many years.
Strategic Importance
The Great Wall of China was not just a wall. It played a vital role in the country’s history. It had strategic importance that went beyond its massive structure. Let’s explore its significance in military defense and trade control.
Military Defense
The Great Wall of China served as a major defense line. It protected the empire from northern invaders. The wall stretched over thousands of miles. It made it hard for enemies to invade. Soldiers could spot invaders from watchtowers.
- Watchtowers provided high vantage points.
- Beacon towers sent smoke signals.
- Armies patrolled the wall day and night.
The wall also had traps and obstacles. These slowed down enemy troops. It created a physical barrier that was hard to cross.
Trade And Control
The Great Wall also controlled trade routes. It was not just for keeping out invaders. The wall monitored the Silk Road. This was a major trade route connecting China to the West.
| Purpose | Details |
|---|---|
| Customs Stations | Collected taxes from traders. |
| Trade Regulation | Controlled what goods entered and left China. |
| Economic Boost | Boosted local economies along the wall. |
Traders had to pass through gates in the wall. This allowed China to control the flow of goods. It also helped in gathering valuable information. The wall was more than a defensive structure. It was a tool for economic and political control.
Cultural Impact
The Great Wall of China is more than just a wall. It has a significant cultural impact that resonates through Chinese history. This ancient structure symbolizes strength and unity. It also plays a crucial role in tourism and preservation efforts.
Symbol Of Strength
The Great Wall of China stands as a symbol of strength. It shows the determination of the Chinese people. They built this wall to protect their land. The wall represents their unity and hard work. Many generations contributed to its construction. The wall stretches over 13,000 miles, showcasing their resilience.
Tourism And Preservation
The Great Wall of China attracts millions of tourists every year. People from all over the world visit this historic site. It boosts China’s tourism industry significantly. The wall offers breathtaking views and rich history. Tourists love to walk along its ancient paths.
| Year | Number of Visitors |
|---|---|
| 2010 | 10 million |
| 2015 | 15 million |
| 2020 | 20 million |
Preserving the wall is a huge responsibility. Many organizations work to maintain it. They ensure its structure remains intact. They also educate the public about its importance. Conservation efforts help protect this cultural treasure for future generations.
- Regular maintenance
- Public education
- Government funding
The Great Wall of China is not just a barrier. It is a testament to human effort and cultural heritage. It continues to inspire people worldwide.

Credit: www.britannica.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Great Wall Of China?
The Great Wall of China is an ancient fortification built to protect against invasions.
How Long Is The Great Wall?
The Great Wall stretches over 13,000 miles across northern China.
Who Built The Great Wall Of China?
The wall was constructed by various Chinese dynasties, starting from the 7th century BC.
Why Was The Great Wall Of China Built?
The primary purpose was to defend against invasions from northern tribes and to protect trade routes.
Conclusion
The Great Wall of China stands as a testament to human ingenuity and perseverance. Its history spans centuries, showcasing architectural brilliance and strategic importance. Visiting this iconic structure offers a glimpse into China’s rich cultural heritage. Explore the Great Wall and immerse yourself in its fascinating past.
Discover why it remains a global marvel.